Summary Statement
A presentation reviewing the major safety risks mobile cranes pose for operators and workers around them and how to reduce those risks. It is designed for site supervisors or safety representatives.
2003
Key Concepts:
- Considerations for proper crane selection and the various types of mobile cranes used in construction.
- Factors that affect stability, capacity and the proper set-up of mobile cranes.
Considerations:
- The weights, dimensions and lift radii expected.
- The type of lifting to be done.
- Serviceability of the equipment.
- The site conditions.
- Be capable of making all its lifts in its standard configuration.
- 5% working margin.
Types of Cranes
- Crawler Cranes
- Locomotive Cranes
- Wheel-Mounted Cranes (Multiple Control Stations)
- Wheel-Mounted Cranes (Single Control Stations)
- Commercial Truck-Mounted Cranes
- When selecting a mobile crane, what are some things that its size and characteristics must be considered against.
- Name four (4) different types of cranes used in the industry.
Jobsite Conditions:
- Supporting Surfaces
- Access & Stability (transporting a crane)
- Working area
- Lattice Boom Assembly & Disassembly
- Reeving the load line
- Leveling the crane
- Soil Conditions must be sufficient.
- Blocking & Cribbing should be used.

Blocking or Cribbing
1. Spreads out the load so the supporting surface can support it.

2.Transmits the load without bending or breaking.

Calculating Blocking/Cribbing Area
Method 1
Area of float (in square feet) x 3 = Blocking area (in square feet)
Method 2
Capacity of crane (in tons) / 5 = Blocking area (in square feet)
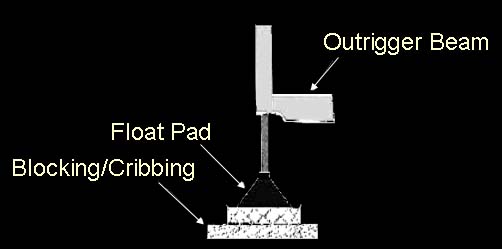
Blocking or Cribbing
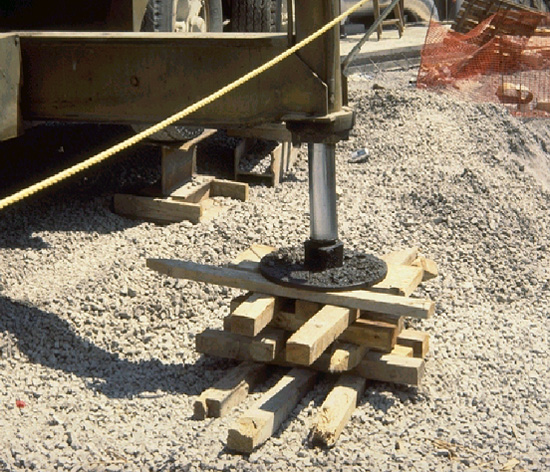

VIOLATION
Transmitting the Load - Properly placed with no gaps or spaces between pieces.
Transmitting the Load; must always be level.
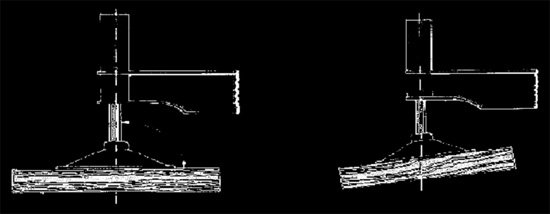
|
RIGHT
|
WRONG
|
Transmitting the Load; must always be stable and never block under outrigger beams inside the floats.
WRONG

VIOLATION
Mats
- Usually made of hardwood.
- Through bolted together
- 8 - 12 inches thick.

If soil conditions are poor enough to require mats, the input of a soil engineer may be needed. Do not make any assumptions.
Working Near Excavations
Recommended Safe Work Practice: Affected Zone
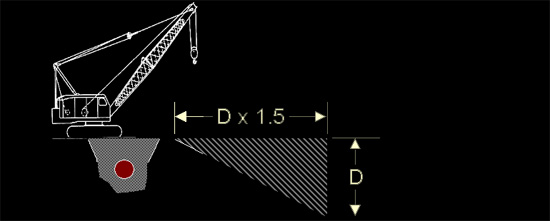
| Be
aware of existing underground utilities and backfill. |
Affected Zone (Depth x 1.5) *Average Soil Only |
Access and Usability
Check for these problems and conditions:
- Compact and traction of surfaces
- Overhead clearance
- Tight turns
- Bridge capacities
- Weight laws
- Special permits needed
- Follow all manufacturer's recommendations and ensure crew is qualified and competent to make decisions.

Work Area
- Site allows for full extension of outriggers or crawlers.
- Minimum clearance of 2 feet from all objects for counterweight.
- Must be level within manufacturer's specifications.

Working Near Airports
- Notification to the Federal Aviation Administration may be required.
- Advisory Circular 70/7460-2K, Proposed Construction or Alteration of Objects that May Affect the Navigable Airspace.
- Form 7460-1 must be filed as early as possible but not less than 30 days before construction begins.
 Working
in Traffic
Working
in TrafficManual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices
- Signs
- Barricades
- Trained Signal Persons
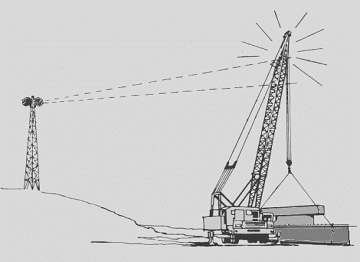
Working Near Transmitters
The following precautions shall be taken when necessary to dissipate induced voltages:
- Electrical ground directly to the upper rotating supporting the boom.
- Ground jumper cables.
- Combustible and flammable material shall be removed from the immediate area..
Lattice Boom Assembly and Disassembly
- Area must be level, firm and large enough to allow room to lay out boom.
- Read and understand manufacturer's instructions (before assembly).
- Sufficient blocking must be available.
- Proper tools available, including ladders.
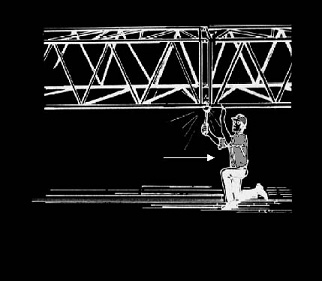
WRONG - never work under the boom
Follow manufacturers' specifications on boom assembly and disassembly.

Boom must be secured against collapse when working inside.
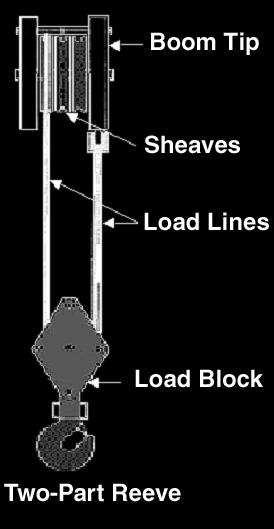
Reeving the Load Line
Operator is familiar with following terms:
- Available line pull
- Allowable line pull or Safe Working Load (SWL)
- Total Load
- Friction Loss
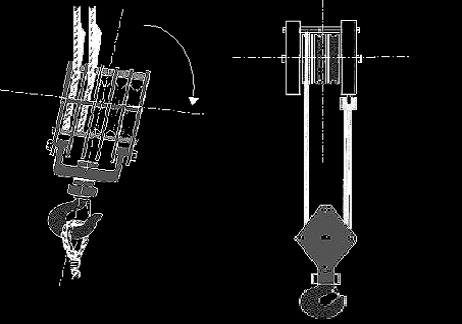
Reeving Hazards
Side loading the hoist block.
|
WRONG
|
RIGHT
|
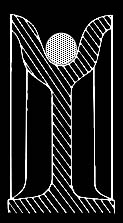
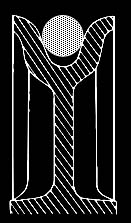
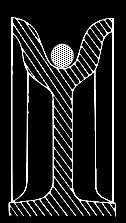
- Matching the load line with sheaves.
 |
 |
 |
|
Properly
matched rope and sheave
|
Rope
is too large, will pinch
|
Rope
is too small, will flatten
|
Sheave Gauge

Leveling the Crane
Should not rely on manufacturer's supplied level.

Determine if the ball is hanging parallel to the boom.

Use a 4 foot carpenter's level on a sturdy part of the crane.

Accident Facts
Poor ground conditions.
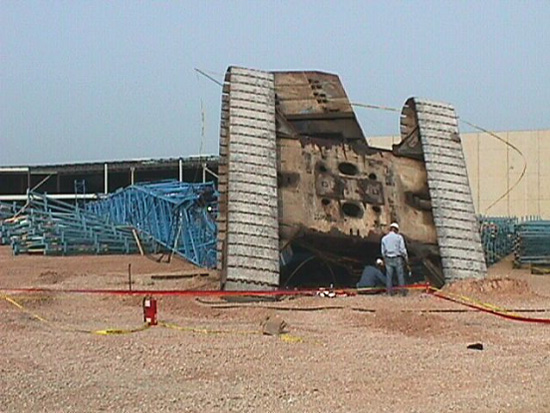

Not level.

Learning Opportunity
- Before attempting to set up the crane, the employer should review the work to be done, plan the entire operation and check the following three (3) site conditions.
- The use of blocking or cribbing performs what two (2) important functions?
- What are four
(4) considerations when placing blocking or cribbing?
- What are three (3) considerations when determining the access and usability of cranes to the job site?


