Summary Statement
This is an in-depth power-point initially presented at the 1/2017 World of Concrete Conference. It provides an overview of new silica rule to help safety and health professionals–
1. Analyze compliance requirements for the new OSHA Crystalline Silica Rule
2. Review concrete construction workplace Safety
3. Understand the risks of exposure to silica
January 19, 2017
Includes Demolition, Cement, Concrete, Brick, Block, Pipe, Cultured Stone, Cut Stone, Recycled Construction Materials, Sand & Gravel production workers
Presented at: World of Concrete 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada
Learning Objectives
 Upon completing this program, the participant should be able to:
Upon completing this program, the participant should be able to:
- Analyze compliance requirements for the new OSHA Crystalline Silica Rule
- Review concrete construction workplace safety
- Explore ways to obtain enhanced productivity
- Examine concrete workers that are more productive and comfortable with the new silica rule
What is Crystalline Silica?
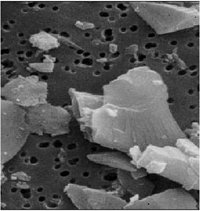
Electron microscope image
- Very jagged micro sized crystallized glass type shards (Quartz, Cristobalite, Tridymite), the most common element on the earth’s surface
- Extremely dangerous to lungs, eventually fatal to humans upon continued, extended, uncontrolled ingestion
- Sand + Heat = Glass = small micro bits = Crystalline Silica
- Micro silica glass shards respiratory system tissue cutters
Silica-containing building materials
- Construction Sand / Concrete Sand must have jagged-roughhewn surfaces for bonding and joining for solidification and strength.
- Saudi Arabia has to import all their construction / concrete sand due to Arabian Desert sand being too smooth. Native Saudi sand will not adequately bond in concrete and cement mixtures due to the winds through eons of time in the desert sweeping each sand grain surface against each other creating smooth surfaces - micro ball bearings.
- Best Silica sands in America are in the upper Midwest and Great Lakes Region.
Micrograms
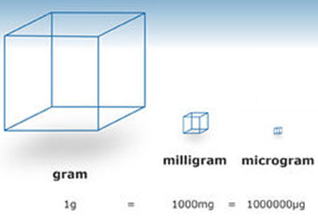
Photo courtesy of The University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand
- Micron – About the size of a single particle of fine milled flour
- Gram – Small metric unit of weight measure - gold is measured in grams
- 1,000,000 micrograms (µg) in 1 gram
- Permissible exposure limit (PEL) for respirable Crystalline Silica is 50 micrograms per cubic meter of air, averaged over an 8 hour shift
- Measured by special analytical instruments
- New OSHA Crystalline Silica Rule for Construction and related industries requires employers to use engineering and administrative controls to limit worker exposure to the PEL
- Final Rule – Document Citation 81 FR 16285 – Ongoing litigation.
- New Construction Standard (29 CFR 1926.1153) effective 06-23-2016, comply by 06-23-2017
- General Industry – Concrete product producers, etc. (29 CFR 1910.1053) took effect, 06-23-2016, comply 06-23-2017
Action Level of Exposure
Trigger for concern and awareness of abatement that leads to the Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
A concentration of airborne respirable Crystalline Silica of 25 µg/m3 as calculated over an 8 hour Time Weighted Average (TWA)

Crystalline Silica Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
An airborne concentration of respirable Crystalline Silica in excess of 50 µg/m3 over an 8 hour Time Weighted Average (TWA)

Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer

United States Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
makers- Perkins-Elmer, Varian Associates, et.al.
Micro sized particle measurement machine
Micrograms and smaller – Atomic size particles, (parts per million) – How machine measures / detects:
- Spectrophotometer uses flame/heat to bring elements of liquid sample into suspension
- Then machine measures heated atomic particles of sample in suspension using light spectrum absorption sensors (eyes)
- Machine then digitally calculates parts per million of various elements in sample. Measured sample amounts are compared to parameters to detect adverse amount of elements
Silica is the most common element on crust of earth’s surface
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer detects silica and other elements (Iron, Copper, etc.) in fluids – engine oils, transmission fluids, differential fluids, axle fluids, transfer case fluids, gear box oils, hydraulic fluids, cooling fluids, machine tool cutting/cooling fluids, chemicals
- Historically industry culture was concerned about Crystalline Silica ingestion in equipment and equipment component failure
- Long term health affects of Crystalline Silica were not considered and identified
- Similar to Asbestos and Atomic radiation exposure –contamination
Crystalline Silica Lungs
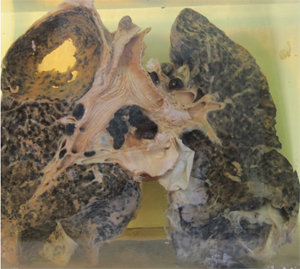
Transformation of healthy lung tissue into scars by Crystalline Silica ingestion, leading to early death, cancer, etc.
- No reversal / no return
- Once lungs are damaged – the damage is permanent
- Unlike healing of the lung tissue from total withdrawal of cigarette / cigar / cannabis smoking
- Silica damaged lungs do not recover through healing
Human applications- workers on construction jobsites and in concrete materials plants

Concern for Crystalline Silica exposure.
Acute and chronic exposure considerations
- Sawing – Masonry, Concrete
- Cutting – Concrete, Stone work
- Drilling – Concrete, Masonry
- Breaking – Concrete – Jackhammers, Excavators, Recycling equipment, etc.
- Demolition – Concrete - Masonry
- Chipping – Roadway profiling
- Milling – Smoothing concrete floors
- Forming – Footers, Walls, Towers, Silos, Columns, Chimneys
- Excavating – Earthmoving (Caliche soils, sandstone, sand, slag = Crystalline Silica
- Crushing – Materials production, Sand & Gravel, Lime, Slag, etc.
Who does Crystalline Silica sampling and analysis?
Industrial Hygienists, Safety-Health workers, Private safety/health consultants, OSHA consultation sections, MSHA services sections, colleges and universities, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
Atmospheric sampling and analysis of suspended Crystalline Silica element microgram particles is done with special pre-calibrated induction measuring instruments
Engineering Controls

Picture courtesy of Deere & Company,
Moline, Illinois, USA
- Enclosed – positive pressure air conditioned,
rollover protective structure cabs on equipment - Water flows
- Water sprays
- Air exchange filtration systems
- Vacuum systems
- Partitions
- Cyclones
- Precipitators
- Positive pressure rooms / zones
Enclosed positive pressure equipment cabs
Open rollover protective cabs - have operators wear suitable respirators and eye protection

Picture courtesy of Atlas Copco USA,
Voorheesville, NY.
Atlas Copco Jaws - Concrete Bridge Demolition
Water flow controls
Manufacturing Operations
- Stone Cutting / Milling
- Brick Cutting
- Block Cutting / Milling
- Slab Cutting/Milling
- Stone Engraving – Cemetery markers, stone signs, etc.

Water Spray Systems
- Crushers
- Material Recycling Equipment
- Conveyors
- Transfer Stations
- Gravel stockpiling
- Demolition work

Water Sprinkers and Mobile Water Spray Units for Crystalline Silica Abatement
- Cement plant slag dumps
- Used foundry sand dumps
- Cement raw material processing – Lime production, etc.
- Recycling concrete road and building materials in crushing system
- Demolition – Ski slope snow making equipment that shoots water directly on rubble

Crystalline Silica Dust Abatement in Demolition Operations
Ski slope snowmaking equipment retrofitted with high water flow nozzle that shoots intense water mist on rubble and structure to control dust in suspension

Severe Crystalline Silica Dust Conditions in Demolition
Water spray can significantly reduce airborne Crystalline Silica dust

Photo courtesy of Brandenburg Industrial Services Co.,
Chicago Illinois
Air Exchange Filtration Systems

High Volume Systems
- Custom Engineered
- Stock Designs

Picture courtesy of Dustcontrol Inc.,
Wilmington, NC, USA
Vacuum Systems
- Mobile
- Custom Designed
- Stock Units
- HEPA Filters – High efficiency particulate arresting
- Removes 99.97% of particles with a size of 0.3 microns
- Random fibers
- Suggest “EPA certified’’ dust extractor
- EPA certified means no leakage
- Need “on-board automatic filter cleaning”

Picture courtesy of Dustcontrol, Inc.,
Wilmington, NC, USA
Hand Held Mobile Units

Picture courtesy of Dustcontrol, Inc., Wilmington, NC, USA

Picture courtesy of Robert Bosch Tool Corporation, North America

Pictures courtesy of Robert Bosch Tool Corporation, North America
Custom Designed/Stock

Picture courtesy of Dustcontrol, Inc. Wilmington, NC
Partitions
- Temporary
- Permanent

Regulated Areas
- The employer must establish a regulated area wherever exposure is, or can be reasonably expected to be in excess of the PEL
- Demarcation of the area
- Signs
- Limited access

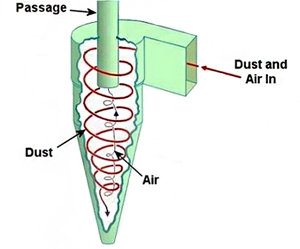
Cyclones
Centrifugal forse spins dust particles to inverted cone base
Precipitators

- Custom Engineered Systems
- Stock Units
- Uses electricity on internal grids to remove dust particles
- Some use water flow on grids to remove dust particles
Personal Protective Equipment - PPE

Picture courtesy of 3M Safety Products,
Minneapolis, Minnesota
- Respirators – P 100 Mask Recommended – light / regular duty applications
- N 95 Mask – Not Good
- Single Strap Mask – Not Good
- P 100 Mask – One Size Fits All
- Abrasive Blasting – Air Fed Helmets – Special consideration
- Protective Clothing
- Hearing Protection
Respirator types by material worked

Picture courtesy of 3M Safety Products,
Minneapolis, Minnesota
- Check with vendor or maker – Technical considerations
- Sizing considerations
- Fit considerations – facial hair, facial landscape
- Physical considerations – lungs / nose / throat – Medical test/evaluation
Air Fed Helmets and Special Respirator types
- Abrasive Blasting
- High volume cutting and drilling operations
- Intensive demolition work in confined spaces
- Intensive drilling and cutting in confined spaces and tunnels
- Working close to underground tunneling machines
- Shotcrete applications in water transmission, transportation and utility tunnels

Picture courtesy of 3M Safety Products, Minneapolis, Minnesota
Most intense Crystalline Silica application – exposure -
Abrasive Blasting

- Use air fed respirator
- Protective clothing
- Hearing protection
- Periodic breaks
Shotcrete Applications
Prolonged exposure to Crystalline Silica

- Respirator use
- Eye safety considerations
- Hearing protection
Underground / confined concrete demolition and construction work

Picture courtesy of the Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA)
- Use high volume fans
- Constantly check atmosphere for Crystalline Silica content
- Monitor Diesel emissions
- Adequate lighting
Administrative Controls

Picture courtesy of Shutterstock.com- Standard License
- Analysis
- Processes
- Policies
- Training
- Understanding
- Testing
- Sampling
- Inspection
- Documentation
Develop a written exposure plan
- Federal and State OSHA consultation programs can assist you on this
- Independent safety/health professional consultants
- National Institute Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) representatives
- Certified Industrial Hygienists
- Colleges and universities
- OSHA Training Institutes

Picture courtesy of Shutterstock.com - Standard license
Provide medical exams to highly exposed workers
 Baseline exams
Baseline exams - Required for each worker who will be occupationally exposed to Silica at or above the action level for 30 or more days per year
- Detailed requirements for a medical examination by a physician or other licensed heath care professional
- Possible referrals to specialist and/or follow-up exams
- Limited information from physician to the employer
- Respirator ability requirement
- Exit exams
Safety and health awareness training program on Crystalline Silica risks and how to limit exposure
- Classroom training
- Field training
- Vendor training
- OSHA Consultation and Training
- Trade Associations (AGC, etc.)
- Trade Unions (Operating Engineers, etc.)
- Insurance Companies
- Insurance Brokers
- Worker compensation entities
- Colleges and universities
- Private safety and health consultants
Provide workers information about lung health
- American Lung Association
- American Cancer Society
Picture courtesy of National Center for Biotechnology Information,
U.S. National Library of Medicine
Crystalline Silica written safety/health training program

- Develop a written safety/health training program on Crystalline Silica exposure/abatement
- Have workers, read, understand and sign-off on it
- Most important is understanding
Training
- Train potential and actual exposed workers on Crystalline Silica hazards.
- Develop within your specific construction jobsite safety/health program a section on Crystalline Silica exposure potential and abatement procedures/processes.
- Use as a tailgate safety/health training session and have workers sign off on this training acknowledging that they understand and will abide by this program.
Instruct workers in their native language so that they will understand the risks and solutions for crystalline silica exposure.
- Make sure your workers understand the risks and control methods for Crystalline Silica exposure
- Everybody going home healthy, safe and happy
Procedures
 Walk your jobsites on a regular basis to detect exposure risks and abatement needs.
Walk your jobsites on a regular basis to detect exposure risks and abatement needs.
Contact a competent Industrial Hygienist to measure and report Crystalline Silica levels that are suspect to you.
Contact your state’s OSHA workplace safety and health consultation program for recommendations and advice.
For clarification and detailed interpretation of the new OSHA Crystalline Silica standard and for on-site visual interventions, inspections and recommendations, contact your state’s OSHA safety and health consultation section.
These services are free.
Resources
OSHA’s new Crystalline Silica Web Page
- The final rule and preamble comments
- Summaries and fact sheets
- CPWR (silica-safe.org)

Crystalline Silica Health Risks
Protecting the Health of Workers Presentation by Don Evans
Introduction
- Dying is always an option
- Anatomy & physiology of the respiratory system
- Effects of silica on the lungs
- Determining the risks
- Preventing the unwanted
Crystalline silica can be fatal
It is a miserable way to die
You will slowly suffocate over a long period of time
Common diseases include
- Pseumoconiosis
- Black lung disease
Facts About Crystalline Silica
Chemical identification: Si
It is the most common element in the earth's crust
Widely used in a variety of applications: Paints, Glass, Cement, Chemicals
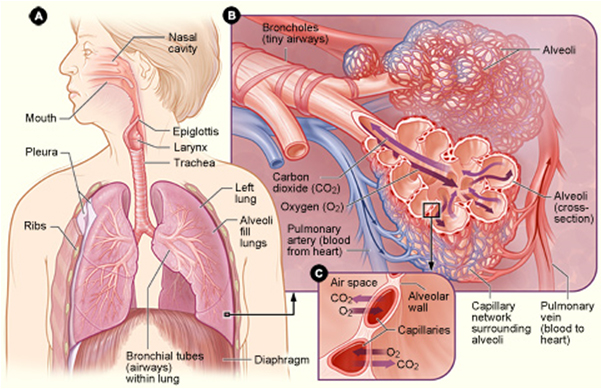
Anatomy & physiology of the respiratory system
- The nose & mouth
- Lined with mucus membranes
- Nose hair to trap large particles
- The superior and inferior turbinates
- The trachea
- Cilia
- Bronchus
- Bronchioles
- Alveolus (pleural)
Effects of silica on the lungs
Microscoptic lacerations of the alveoli
Formation of scar tissue
- Creation of fibroids
- Non-detectable until ~1cm in size
- Now observable on a radio graph (x-ray)
Scar tissue & fibroids prevent the exchange of gasses in the lung tissue
- Oxygen and Carbon dioxide
-The body will be starved for O2
-The condition is irreversible
- Bronchio-dialators may provide temporary relief early on
- Medical oxygen may be necessary as the disease progresses
Determining the risks
It is the employer's responsibility to perform a risk assessment
- Employees should know the risks of the jobs they are expected to perform
What forms of protection will be utilized to prevent over-exposure?
- Wet methods
- HEPA vacuum, etc.
How much silica exposure is too much?
- The new standard specifies 50 µg/m3
- The action level is 25 µg/m3
- This is ~ 20% of the old standard
-A worker who is diagnosed with silicosis, pneumoconiosis or black lung disease will become and enormous liability to an employer's workman's compensation program
- Employers can be required to place additional funds in their reserve account to cover these long term expenditures
Prevention
It starts with a good workplace risk assessment
- Identify the hazards and then design a good prevention strategy
If your prevention strategy involves respiratory protection, consult 29 CFR 1910.134 Respiratory Protection
- You will need to comply with the regulation before putting workers in respirators
- N95’s may look like dust masks, but they are classed as respirators and require fit testing per the manufacturers instructions
Prevention is a synonym for safety- the standard is not designed to intimidate or harass. It is all about preventing unwanted, unplanned and undesired medical problems that at the least may be an inconvenience, and at worst may cause a workers death.
Summary
No one goes to work to die on the job
- Employers are responsible to provide a work environment that has either eliminated or addressed the hazards
Knowing how the body works can be a real asset in knowing what to do to protect yourself
Silica is a known hazard that can be life threatening
Know the risks and how to deal with them
Don’t take protection for granted
- Ask the FDNY what happened after 9/11
The forgoing presentation is based on the most recent information available. It is not intended to be all inclusive. It is the employer’s responsibility to protect workers on the job. OSHA provides consultation services in all states and territories of the United States.
This concludes the Continuing Education Program. Any questions?
Contact
Dave Murray
damurray@business.nv.gov
Don Evans
d2e54@hotmail.com



