Safe Work Permits
-
Safety Permits
The following are links to all of the items in this collection:
Summary Statement
A training presentation on safe work permits, what they are, when they are needed and how to use them.Part of a collection. Click on the 'collection' button to access the other items.
3/25/1997
Why are we here?
The company requires evaluation of very hazardous, nonroutine jobs for which there are no Safe Job Procedures or approved Job Safety Plans.
Certain jobs always require that a Safe Work Permit be issued by a qualified individual.
Goals and Objectives:
At the end of this session you will:
- be familiar with
jobs requiring safe work permits.
- be generally
familiar with the Safe Work Permit system.
- pass a quiz with a score of 100%.

There are currently three documents which are called "safe work permits."
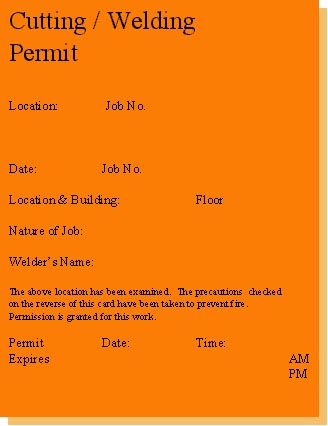
The Hot Work Permit is a form of Safe Work Permit issued by the Fire Marshal or other person responsible for fire safety.
This permit is required for all situations which may result in fires or explosions.
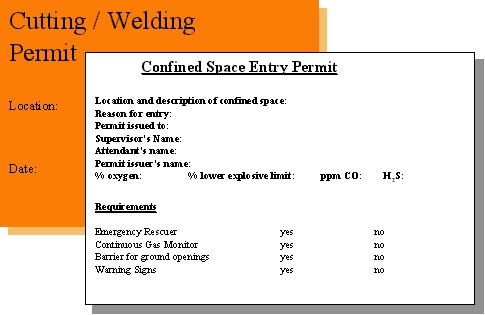
Confined Space Entry Permit
Location and description
of confined space:
Reason for entry:
Permit issued to:
Supervisor’s Name:
Attendant’s name:
Permit issuer’s name:
% oxygen: % lower explosive limit: ppm CO: H2S:
Requirements
| Emergency Rescuer |
yes |
no |
| Continuous Gas Monitor |
yes |
no |
| Barrier for ground openings |
yes |
no |
| Warning Signs |
yes |
no |
| Safety Harness with life line |
yes |
no |
| Tripod / Hoist / Pulley |
yes |
no |
The “Confined Space Entry Permit” is another form of safe work
permit regulating entry into pits, tanks, and vessels.
Confined Space Entry Permits and Hot Work Permits will be discussed in detail in other training sessions.
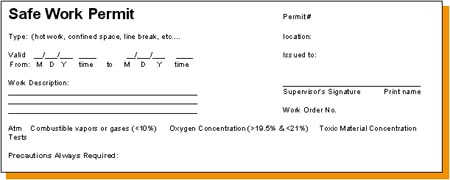
The objective of the Safe Work Permit system is to identify hazards associated with a nonroutine job, and to develop precautions required to control each hazard identified.
Let’s begin with a look at the hazards associated with specific jobs, and examine how Safe Work Permits can help to prevent them from causing damage or injury.
Examples of jobs requiring permits are:
- Hot Work - the
use of open flame, oxyacetylene burning, tar kettles, etc...., and the
use of portable spark or heat producing equipment in flammable storage
or handling areas.
- Confined Space
Entry
- Excavations
- Blasting
- Whenever required
by existing company or contractor procedures or required in the contractor’s
Project Safety Plan.
- Use of internal
combustion engines, or vehicles with internal combustion engines inside
company buildings.
- Use of company owned equipment, such as personnel lifts, fork trucks, vehicles, etc., by employees of a contractor
Excavations
can result in:
-
head injuries from
materials falling from overhead surfaces,
rupture of high pressure hydraulic lines used on backhoes, shovels, and drills.
excessive noise from concrete breaking and cutting equipment, and collapse of excavation walls and piles due to poorly secured soil, sudden weather changes, or other factors.
Permits are written to ensure that necessary equipment is present and in good working order.
Excavations:
-
Poorly planned excavations
can result in damage to underground services, such as electrical lines,
natural gas lines, water lines, sewers and drains.
The consequence of damaged service lines is often complete shutdown of operations resulting in major business losses.
Permits are written to prevent damage to underground equipment and services.

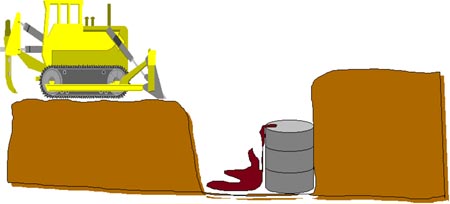
Excavations may expose hazardous materials, which have leaked and are contaminating the soil.
Permits ensure that procedures to protect workers from exposure to toxic substances have been identified.
Blasting can cause damage to adjacent operations and personnel.
Permits are issued to ensure procedures are followed that prevent injury to neighboring facilities, equipment and employees.
Internal combustion engines produce poisonous gases such as carbon monoxide, and oxides of nitrogen.
Permits ensure that procedures are followed that will prevent equipment emissions from contaminating air inside buildings and confined spaces.
Unauthorized use of company equipment can result in lost production and injury to untrained operators.
Permits prevent company equipment from being taken by contractors without the permission of area management, and require verification of equipment operator training.
Work which ordinarily does not require safe work permits may be included at the discretion of the Safety Representative, the Contractor, or the Contract Administrator.

Following are examples of situations which may require discretionary safe work permits.
There could be many others:

Movement of large pieces of equipment, especially while other personnel are working nearby, can result in employee injury.
Permits may be issued to ensure the use of procedures that will prevent employee injury from falling material, or being struck by rigging equipment.
| Abandoned
tanks, pipe lines, drums, and vessels may contain hazardous vapors
and gases.
Permits may be issued to prevent toxic or corrosive exposures to workers when working on abandoned equipment, complementing hot work and confined space permits. |
 |
 |
Many
construction processes create noise levels high enough to cause hearing
loss.
Permit requirements may be issued to reduce noise to acceptable limits, or to provide both construction and other employees with required hearing protection. |
Boilers, high pressure vessels, tanks, and reactors can undergo sudden failure resulting in disastrous consequences.
Permits may be issued requiring precautions and equipment to prevent system failures not covered by safe job procedures or project safety plans.
Permits may be required where the consequence of noncompliance with fall protection requirements is severe, or where dropped materials may endanger other workers below.

Permits are required before work begins near energized lines which cannot
be shut off if there is danger of fire, shock or electrocution.
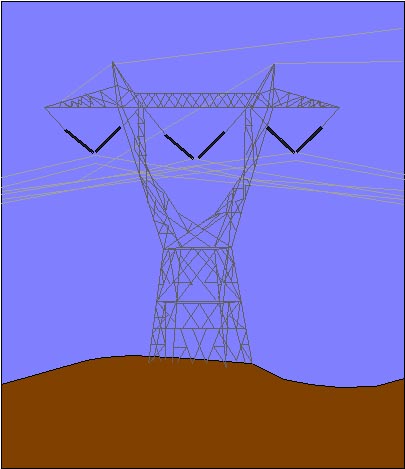

Permits are mandatory where signs are posted which require them.

Permits are issued:
- for a specific
date and time range,
- for a specific
job,
- and to specific individuals.
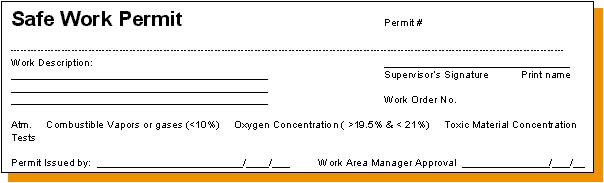
Permits must be reviewed and signed by:
- the safety representative
issuing the permit,
- the workers’
supervisor,
- affected workers,
- and the work area manager.

Workers must be informed of required emergency procedures, location and operation of emergency equipment,and area inherent hazards.
Material Safety Data Sheets must be supplied and special precautions reviewed with workers and their supervision.
| Safe Work Permit
---------------------------------------------------------------------- o Buddy System
o Sprinklers in Service |
Required special precautions must be clearly indicated and communicated to workers, and their supervision.
It is the safety representative’s responsibility to determine if and when special measures are required.
| Safe Work Permit
---------------------------------------------------------------------- o safety glasses |
Personal protective equipment and other safety equipment required is specified.
For each hazard present at the work site, the safety representative must specify a hazard control.

The safety representative must verify that all underground utilities have been located and staked out.
Provisions must be made to barricade the open trench, prevent collapse of trench walls, provide employees with a means of exit, reroute ground water, and all other requirements of excavating.
If soil is contaminated, the safety representative will ask for a written safety and health plan.
SUMMARY
- Hot work, confined space entry, excavations, blasting, use of internal combustion engines inside of buildings, use of company owned or leased equipment, and areas where “Safe Work Permit Required” signs are posted always require a safe work permit.
- Other safe work permits may be required at the discretion of the Safety Representative, the Contract Administrator, or the Contractor.
- Permits will be issued by a qualified safety representative.
- Hot work permits are issued by the Fire Marshal.
- Permits are issued to specific persons for a specific time period and for a specific job.
- Permits must be signed at the time issued by the safety representative, job supervisor, affected workers, and the manager of the area in which work is being done.
Where to Get Help?
Your supervisor is responsible for providing equipment necessary to comply with Safe Work Permit requirements.
The safety representative is responsible for completing the job hazard analysis and issuing the permit.


