Roadway Safety: Instructor Manual
Laborers' Health and Safety Fund of North America
-
Roadway Safety
The following are links to all of the items in this collection:
Documents
- Roadway Safety: Run Overs & Back Overs
- Roadway Safety: Operator Safety
- Roadway Safety: Struck or Crushed
- Roadway Safety: Flagger Safety
- Roadway Safety: Night Work
- Roadway Safety: Excavation
- Roadway Safety: Electrical hazards
- Roadway Safety: Strains and Sprains
- Roadway Safety: Fall Hazards
- Roadway Safety Awareness Program: Trainee Booklet
- Roadway Safety: Instructor Manual
- Roadway Safety: Working outdoors
- Roadway Safety: Noise Hazards
- Roadway Safety: Health Hazards
- Roadway Safety: Emergencies
Summary Statement
A manual that helps a trainer provide information on a variety of roadway hazards, such as electrical, falls, slips and trips and ergonomics. Part of a collection. Click on the 'collection' button to access the other items.
2002
| This document is one in a program produced under an OSHA grant by a consortium of the Laborers' Health and Safety Fund N.A, the International Union of Operating Engineers, the American Road and Transportation Builders Assn, and the National Asphalt Pavement Assn. All of the documents from this set that are on eLCOSH can be found by clicking on Job Site, Heavy construction, and scrolling to the Street & highway heading. Or to download a complete version of the computerized program, go to https://www.workzonesafety.org/. |
Most of the work in heavy and highway construction — which excludes bridges and tunnel work — is done on or near the ground. This means that the most falls results from slips or trips on the same level. Falls on walking and working surfaces involve:
- tripping over materials or debris,
- falling on hills or embankments,
- stepping in holes or walking on irregular ground,
- stumbling while carrying loads that block vision, and
- slips or trips in muddy, wet, or icy conditions.
- falls from riding in or on moving equipment,
- falls while mounting or dismounting vehicles and equipment,
- falls from bridges,
- falls from formwork, and
- falls into excavations.
 |
| Fig. FH-1A. Most falls in road construction result from slips or trips on the same level. |
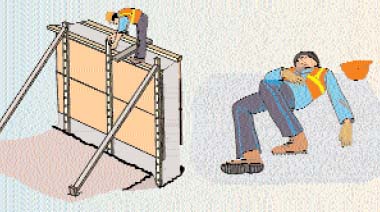 |
| Fig. FH-1B. In road work, there are some falls from elevations. Even falls from a few feet can kill. OSHA requires fall protection for work at 6 feet above any surface. |
Notes:
Ask trainees: What percentage of injuries in highway work are due to falls? (Falls are the second leading cause of serious injuries in highway construction. Almost 17% of all lost workday injuries in highway construction are due to falls. About half of these falls were to lower levels and about half were falls on the same level.)
Can you get killed from even a short fall?
What are the most common tripping hazards?
Missing the last step when climbing off a vehicle is a big problem.
Many workers fall when crawling onto a truck to check the water level.
Note: OSHA requires fall protection above 6 feet. OSHA also requires fall protection below 6 feet if workers can fall into or onto dangerous equipment.
How Do We Prevent Falls on Same Level?
There are many simple methods for preventing falls on the same level in road construction. Try to do as many as possible. Just a few of them include:
- If possible, avoid walking on muddy, wet, or icy surfaces.
- Use footwear with ankle support and soles that grip.
- Don't carry heavy loads, use hauling equipment
- Practice good housekeeping, remove tools and materials.
- Fill in or mark hidden holes in ground.
- Clear walking/working surfaces of tripping hazards.
- Include walking routes in site safety plan.
How Do We Avoid Falls From Elevations?
There are also many methods for preventing falls from elevations. Some of these methods include:
- a 100% fall protection program,
- pre-plan work for personal fall arrest,
- erect guardrails around large excavations,
- seatbelts or restraints for riding in cars,
- modular erection to avoid work at heights on forms,
- using 3-point contact on ladders.
 |
| Fig. FH-2. There are simple methods for preventing falls on the same level. |
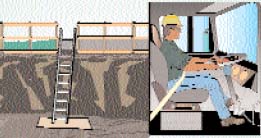 |
| Fig. FH-3. There are many methods for preventing falls from elevations. |
Notes:
How can we improve good housekeeping on this site?
These are OSHA-required fall protection methods. Ask trainees if they can think of smaller ways to prevent falls every day. For example, to eliminate the hazard of falling from a water truck while trying to see how much water is left, you can place a sight glass (mirrored device) on top of it. That way, workers can stay on the ground and still see how much water is left.
Back to Contents


