Roadway Safety: Excavation
Laborers' Health and Safety Fund of North America
-
Roadway Safety
The following are links to all of the items in this collection:
Documents
- Roadway Safety: Run Overs & Back Overs
- Roadway Safety: Operator Safety
- Roadway Safety: Struck or Crushed
- Roadway Safety: Flagger Safety
- Roadway Safety: Night Work
- Roadway Safety: Excavation
- Roadway Safety: Electrical hazards
- Roadway Safety: Strains and Sprains
- Roadway Safety: Fall Hazards
- Roadway Safety Awareness Program: Trainee Booklet
- Roadway Safety: Instructor Manual
- Roadway Safety: Working outdoors
- Roadway Safety: Noise Hazards
- Roadway Safety: Health Hazards
- Roadway Safety: Emergencies
Summary Statement
A handout describing dangers of building and working in trenches. Discusses the nature of the danger, ways to prevent cave-ins and other safety tips.Part of a collection. Click on the 'collection' button to access the other items.
| This document is one in a program produced under an OSHA grant by a consortium of the Laborers' Health and Safety Fund N.A, the International Union of Operating Engineers, the American Road and Transportation Builders Assn, and the National Asphalt Pavement Assn. All of the documents from this set that are on eLCOSH can be found by clicking on Job Site, Heavy construction, and scrolling to the Street & highway heading. Or to download a complete version of the computerized program, go to https://www.workzonesafety.org/. |
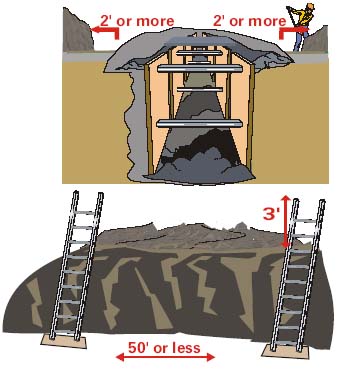
A trench is an excavation deeper than it is wide.
Trenches can kill
- Workers can be buried alive
- Cave-ins can result from stresses in walls, nearby moving vehicles and equipment, or spoil piles
- Water can collect in bottom
- Flammable/toxic gases can build up
- Gas from nearby sewer or gas lines can seep into trench
- Call electrical, gas, and communications utilities
- Use extreme caution with equipment
An excavation with formwork 15' or less from a sidewall is also a trench.
How Do We Prevent Cave-Ins?
Trenches 5 feet or deeper require support.*
Sloping
- Soil angled to increase stability
- Steps in trench wall
- Support system made of posts, wales, struts, and sheeting or hydraulic shoring
- Protective frame or box, to protect workers after a cave-in
What Else Does Excavation Require?
Employer should designate 'competent person.
'Competent person' must inspect
- At least daily and beginning of each shift
- After precipitation, a thaw, and other events that could increase hazard
- For disturbed ground, water, toxics, and other hazards
- If walls sag or crack or the bottom bulges
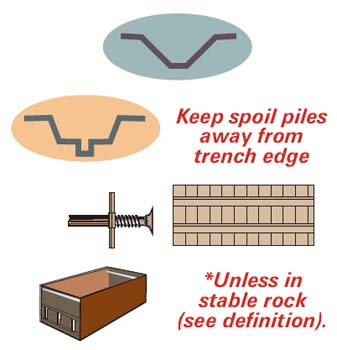
- To keep spoil at least two feet from trench edge
- If there are nearby vibration sources such as railroads or piledriving
- That no worker is more than 25 feet from an exit.