Roadway Safety: Health Hazards
Laborers' Health and Safety Fund of North America
-
Roadway Safety
The following are links to all of the items in this collection:
Documents
- Roadway Safety: Run Overs & Back Overs
- Roadway Safety: Operator Safety
- Roadway Safety: Struck or Crushed
- Roadway Safety: Flagger Safety
- Roadway Safety: Night Work
- Roadway Safety: Excavation
- Roadway Safety: Electrical hazards
- Roadway Safety: Strains and Sprains
- Roadway Safety: Fall Hazards
- Roadway Safety Awareness Program: Trainee Booklet
- Roadway Safety: Instructor Manual
- Roadway Safety: Working outdoors
- Roadway Safety: Noise Hazards
- Roadway Safety: Health Hazards
- Roadway Safety: Emergencies
Summary Statement
A handout describing dangers of health hazards such as silica, lead, asphalt and wet concrete, as well as methods to reduce the hazards. Part of a collection. Click on the 'collection' button to access the other items.
| This document is one in a program produced under an OSHA grant by a consortium of the Laborers' Health and Safety Fund N.A, the International Union of Operating Engineers, the American Road and Transportation Builders Assn, and the National Asphalt Pavement Assn. All of the documents from this set that are on eLCOSH can be found by clicking on Job Site, Heavy construction, and scrolling to the Street & highway heading. Or to download a complete version of the computerized program, go to https://www.workzonesafety.org/. |
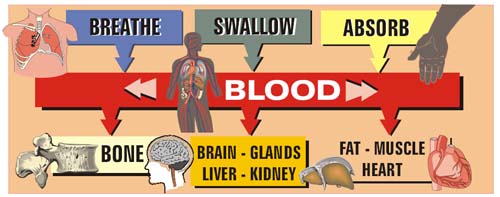
Toxic substances can enter the body by 3 routes.
The effects of toxic substances may be
- Short-term or acute: effects such as eye irritation or dizziness
- Delayed or chronic: effects such as cancer or chronic lung disease
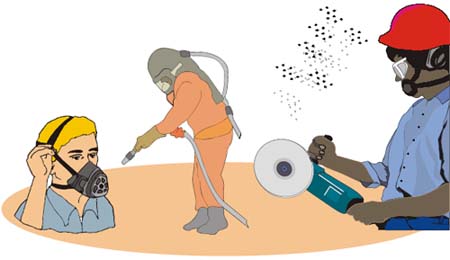
How Harmful Is Silica?
Silica is common but can be very harmful.
Silica dust
- Found in many construction dusts such as concrete, rock
- High exposure tasks include sand blasting, rock drilling, cutting concrete
- Long-term exposure leads to lung disease (silicosis)
- Long-term exposure increases risk of cancer
- Reduce airborne dust through ventilation and wetting
- Use NIOSH-approved toxic dust respirators
How Harmful Is Asphalt?
Asphalt fumes and skin contact can be harmful.
Asphalt
- Fumes may cause eye, respiratory irritation
- Hot asphalt can severely burn skin

To prevent exposure
- Work upwind whenever possible
- Maintain a lower temperature to minimize fumes
- Use ventilation on paving machines
- Wear gloves, long sleeves to prevent skin contact
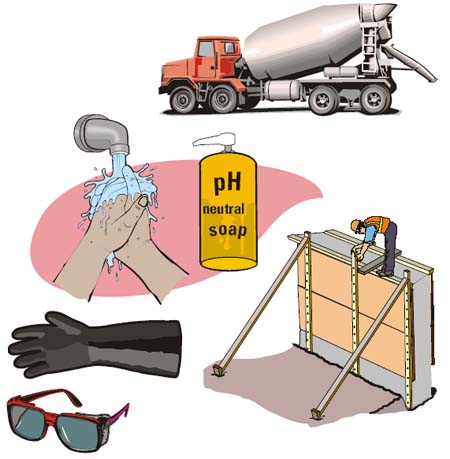
It can cause dermatitis and skin burns.
Dermatitis can be
- Irritation from caustic chemicals in concrete
- Allergic reaction
- Wear long-sleeved gloves
- Keep concrete out of your boots
- Change gloves/boots when contaminated inside
- Wash hands in clean water with pH-neutral soap
- Protect cuts with bandages
- Wear eye protection
How Harmful Is Lead?
Lead damages nervous and reproductive systems.
Lead
- Toxic metal found in paints on bridge renovation
- Dust and fume can be inhaled or ingested during sandblasting, welding, cutting
- Dust can be carried home and poison your family
- Remove paint before cutting or welding
- Use long-handled torches for cutting
- Use local exhaust ventilation
- Wear the proper respirator
- Wash face and hands before eating, smoking, or drinking
- Shower and change clothes before leaving work
- Get your blood lead tested periodically to assure you are not overexposed

Are There Other Health Hazards?
Most can be avoided with basic protections.
Other hazards include
- Common substances such as solvents and CO
- Special products such as sealants, paints
- Reviewing the product Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
- Limiting exposure as much as possible
- Staying upwind of hazardous exposures
- Making sure that hazard controls such as fans are working
- Wearing protective equipment such as respirators, skin coverings
- Promptly reporting any health complaints to your supervisor



